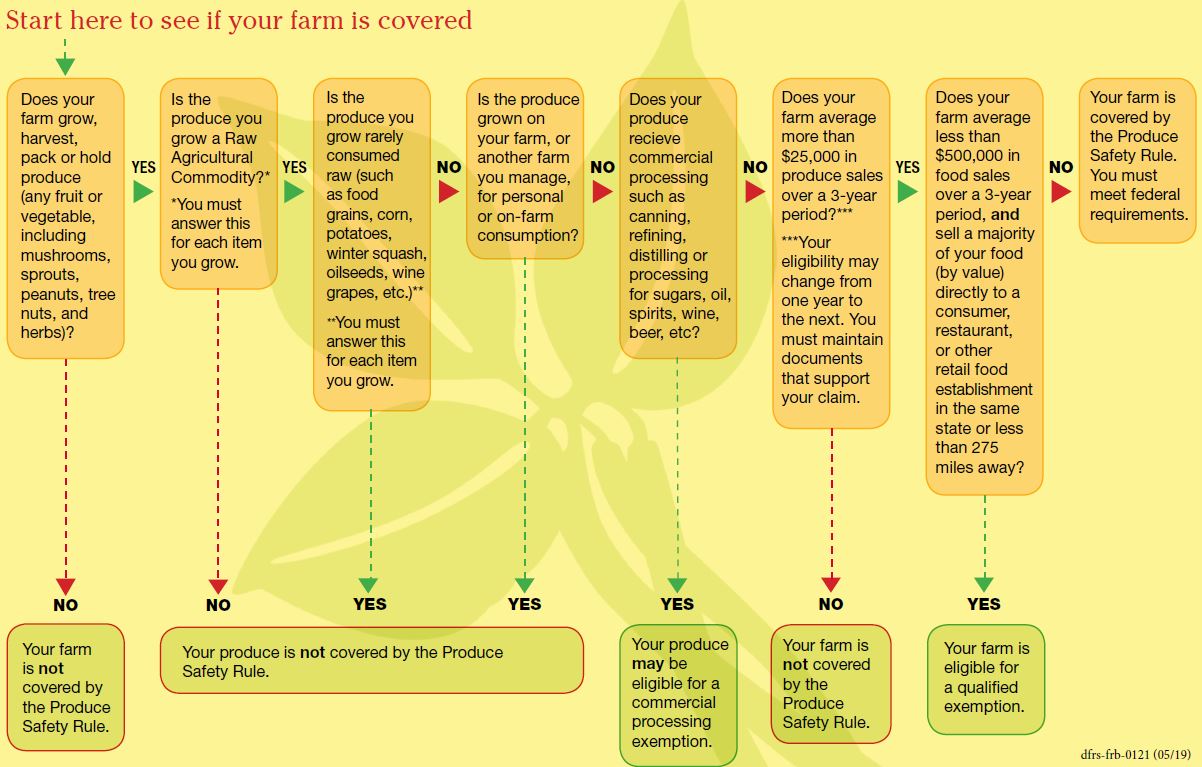
Safe Wisconsin Produce (SWP) is responsible for education and compliance with Title 21 CFR Part 112, Standards for the Growing, Harvesting, Packing, and Holding of Produce for Human Consumption, otherwise known as the Produce Safety Rule (PSR). The PSR is the one of seven rules created as part of the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) and establishes a common set of standards for produce farming practices. The PSR categorizes all farms as covered or exempt (see below).
Defining the Various Statuses
Covered farms must comply with all applicable PSR requirements when conducting covered activities on covered produce. Farms are subject to PSR requirements if the average annual dollar value of the produce they sold during the previous 3-year period was more than $25,000 adjusted for inflation, and are considered “covered farms" (21 CFR 112.4(a)).
Covered farms are subject to PSR inspection; SWP staff will contact covered farms to announce PSR inspections. This FDA fact sheet explains what to expect during a PSR inspection.
A farm is not covered if exempt and has not had its exemption withdrawn. Read more about withdrawal of exemptions in 21 CFR 112.201-213.
Sales Exempt
Farms are exempt and not subject to PSR requirements if the average annual dollar value of the produce they sold during the previous 3-year period was less than $25,000 adjusted for inflation.
Keep dated sales receipts and adequate records that demonstrate that you have performed an annual review of your farm's eligibility for a sales exemption. Although full regulatory services are not available to exempt farms, non-regulatory services such as On-Farm Readiness Reviews, SWP Audits, Produce Safety Alliance (PSA) Grower Trainings, and other outreach and technical assistance are available to all exempt farms.
Eligible farms are farms with produce sales greater than $25,000 but food sales less than $500,000 adjusted for inflation and which sell the majority dollar value of their food sales directly to qualified end-users, such as the consumer of the food or a restaurant or retail food establishment in the same state or Indian reservation, or not more than 275 miles from the farm that produced the food.
Qualified exempt farms are not fully exempt from regulatory services. SWP may conduct a limited scope inspection, verifying relevant sections of the PSR, including:
Withdrawal or Reinstatement of Status
A qualified exemption may be withdrawn if necessary to protect public health and prevent or mitigate a foodborne illness outbreak. Although full regulatory services are not available to exempt farms, non-regulatory services such as On-Farm Readiness Reviews, SWP Audits, PSA Grower Trainings, and other outreach and technical assistance are available to all exempt farms.
In addition to full-farm exemptions, specific commodities may be exempt if they fall within one of the following categories, noting that they are still produce for purposes of sales calculations and the farm cannot be commodity exempt if farming any non-exempt produce commodities under the same management:
1. Rarely Consumed Raw. Produce that is listed in the comprehensive FDA Rarely Consumed Raw list is not covered by the PSR: asparagus; beans, black; beans, great northern; beans, kidney; beans, lima; beans, navy; beans, pinto; beets, garden (roots and tops); beets, sugar; cashews; cherries, sour; chickpeas; cocoa beans; coffee beans; collards; corn, sweet; cranberries; dates; dill (seeds and weed); eggplants; figs; ginger; hazelnuts; horseradish; lentils; okra; peanuts; pecans; peppermint; potatoes; pumpkins; squash, winter; sweet potatoes; and water chestnuts.
2. Processing Exempt. Produce is not covered when destined for a commercial processing “kill step" that adequately reduces human pathogens and when the grower has disclosed in accompanying documentation provided to the processor/buyer that the produce is “not processed to adequately reduce the presence of microorganisms of public health significance."
Examples of such “kill-step" processing include processing in accordance with parts 113, 114, 120, as well as canning, refining, and distilling. More examples are provided in 21 CFR 112.2(b)(1).
(FDA intends to exercise enforcement discretion regarding the 112.2(b)(3) written assurance requirements until the rulemaking is complete. Read more in the Current Good Manufacturing Practice and Preventative Controls, Foreign Supplier Verification Programs, Intentional Adulteration and Produce Safety Regulations: Enforcement Policy Regarding Certain Provisions (March 2022))
3. Enforcement Discretion. Produce under FDA enforcement discretion is not considered covered at this time.
In 2019 the FDA published a Guidance to Industry bulletin announcing an Enforcement Policy for Entities Growing, Harvesting, Packing, or Holding Hops, Wine Grapes, Pulse Crops, and Almonds.
4. Excluded. Produce that is produced by an individual for personal consumption or produced for consumption on the farm or another farm under the same management is not covered by the PSR.
Although full regulatory services are not available to exempt farms, non-regulatory services such as On-Farm Readiness Reviews, SWP Audits, PSA grower trainings, and other outreach and technical assistance are available to all exempt farms. All farms should re-evaluate their eligibility each year based on the commodities they are growing, harvesting, packing and/or holding.
What category is your farm?
SWP publishes an annual survey and produce farm registry and encourages all produce farms to participate every year. The SWP farm registry displays participating farms' statuses.
Don't see your farm? Take the 2024 produce survey and registry and check the box to participate in the produce safety registry, or reach out to a member of the SWP team for additional assistance.
View our SWP flow chart below to walk through the steps to learn how to determine if a farm is covered by the PSR. A printable version of this flowchart is also available in the "Is my farm covered by the new federal produce safety rules?" brochure (English | Hmong | Spanish).